Deployer vos instances avec Terraform
ro:Implementarea instanțelor dvs. cu Terraform ru:Развертывание ваших экземпляров с помощью Terraform pl:Wdrażanie instancji za pomocą Terraform ja:Terraformによるインスタンスのデプロイ zh:用Terraform部署你的实例 de:Bereitstellen Ihrer Instanzen mit Terraform nl:Je instances uitrollen met Terraform it:Distribuire le istanze con Terraform pt:Implementar as suas instâncias com a Terraform es:Despliegue de sus instancias con Terraform en:Deploying your instances with Terraform
Description
Nous allons voir comment déployer rapidement une ou plusieurs instance(s) Cloud IKOULA One via l'outils d'infrastructure as code nommé "Terraform".
Tout d'abord vous devrez installer Terraform, si ce n'est pas déjà fait et disposer d'un compte Cloud IKOULA One. Terraform est disponible pour la plupart des OS au lien suivant : https://www.terraform.io/downloads.html
Terraform supporte plusieurs dizaines de provider dont la liste est disponible sur leur site (https://www.terraform.io/docs/providers/). Nous utiliserons le provider "Cloudstack" pour déployer sur Cloud Ikoula One.
Déploiement d'une instance simple
Nous allons écrire notre premier fichier de configuration Terraform permettant le déploiement d'une seule instance Cloud IKOULA :
Il s'agit d'un fichier texte d'extension " .tf " (attention de ne pas créer plusieurs fichiers " .tf " au sein de votre répertoire de travail sinon Terraform les chargera tous), nous utiliserons le format Terraform classique mais il est également possible d'utiliser une syntaxe JSON.
Voici le contenu de notre fichier Terraform à adapter avec vos propres paramètres :
- Pour le déploiement d'une instance en zone basic :
provider "cloudstack" {
api_url = "https://cloudstack.ikoula.com/client/api"
api_key = "< Votre clé API de votre compte/utilisateur Cloud Ikoula One >"
secret_key = "< Votre clé secrète de votre compte/utilisateur Cloud Ikoula One>"
}
resource "cloudstack_instance" "< Nom de votre choix pour votre ressource >" {
zone = "< Nom de la zone basic Cloud Ikoula One de votre choix >"
service_offering = "< Nom de l'offre de calcul Cloud Ikoula One de votre choix > "
template = "< Nom du modèle Cloud Ikoula One de votre choix"
name = "< Nom de votre choix pour votre instance Cloud Ikoula One"
keypair = "< Nom de votre paire de clé SSH Cloud Ikoula One>"
expunge = "true"
security_group_ids = ["< ID de votre groupe de sécurité Cloud Ikoula One à utiliser >",]
}
- Pour le déploiement d'une instance en zone avancée (avec création d'une règle de redirection de port, pour ssh dans cet exemple) :
provider "cloudstack" {
api_url = "https://cloudstack.ikoula.com/client/api"
api_key = "< Votre clé API de votre compte/utilisateur Cloud Ikoula One >"
secret_key = "< Votre clé secrète de votre compte/utilisateur Cloud Ikoula One>"
}
resource "cloudstack_instance" "< Nom de votre choix pour votre ressource d'instance >" {
zone = "< Nom de la zone avancée/adv Cloud Ikoula One de votre choix >"
service_offering = "< Nom de l'offre de calcul Cloud Ikoula One de votre choix > "
template = "< Nom du modèle Cloud Ikoula One de votre choix"
name = "< Nom de votre choix pour votre instance Cloud Ikoula One"
keypair = "< Nom de votre paire de clé SSH Cloud Ikoula One>"
expunge = "true"
network_id = ["< ID de votre réseau d'invités Cloud Ikoula One à utiliser >",]
}
# Redirection de port (ici SSH)
resource "cloudstack_port_forward" "SshTerraformVM1" {
ip_address_id = "< ID de l'adresse ip NAT Source de votre réseau d'invités >"
forward {
protocol = "tcp"
private_port = "22"
public_port = "< port ssh publique de votre choix>"
virtual_machine_id = "${cloudstack_instance.< Nom que vous avez choisis au-dessus pour votre ressource d'instance >.id}"
}
}
Note : la ligne 'expunge = "true"' nous permettra de supprimer notre instance lors de l'appel "terraform destroy".
Une fois votre fichier de configuration enregistré, nous allons initialiser Terraform puis l'appliquer :
$ terraform init Initializing provider plugins... The following providers do not have any version constraints in configuration, so the latest version was installed. To prevent automatic upgrades to new major versions that may contain breaking changes, it is recommended to add version = "..." constraints to the corresponding provider blocks in configuration, with the constraint strings suggested below. * provider.cloudstack: version = "~> 0.1" Terraform has been successfully initialized! You may now begin working with Terraform. Try running "terraform plan" to see any changes that are required for your infrastructure. All Terraform commands should now work. If you ever set or change modules or backend configuration for Terraform, rerun this command to reinitialize your working directory. If you forget, other commands will detect it and remind you to do so if necessary.
Avant de lancer notre déploiement (ici en zone basic), nous pouvons vérifier ce qui sera exécuté sans rien appliquer via la commande :
- terraform plan
$ terraform plan
Refreshing Terraform state in-memory prior to plan...
The refreshed state will be used to calculate this plan, but will not be
persisted to local or remote state storage.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
An execution plan has been generated and is shown below.
Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols:
+ create
Terraform will perform the following actions:
+ cloudstack_instance.TerraformVM1
id: <computed>
display_name: <computed>
expunge: "true"
group: <computed>
ip_address: <computed>
keypair: "MY_SSH_KEYPAIR"
name: "TerraformVM1"
network_id: <computed>
project: <computed>
root_disk_size: <computed>
security_group_ids.#: "1"
security_group_ids.3260590242: "84be7eef7-4pne-51c6-9abf6f3f9-c4zoek90887"
service_offering: "t1.pico"
tags.%: <computed>
template: "Debian 9 - Minimal - 64bits"
zone: "US-FL-MIAMI02-Z2-BASIC"
Plan: 1 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Note: You didn't specify an "-out" parameter to save this plan, so Terraform
can't guarantee that exactly these actions will be performed if
"terraform apply" is subsequently run.
Si c'est bien ce que nous voulons faire alors nous pouvons appliquer via la commande "terraform apply" et saisir "yes" pour confirmer quand cela nous est demandé :
$ terraform apply
An execution plan has been generated and is shown below.
Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols:
+ create
Terraform will perform the following actions:
+ cloudstack_instance.TerraformVM1
id: <computed>
display_name: <computed>
expunge: "true"
group: <computed>
ip_address: <computed>
keypair: "MY_SSH_KEYPAIR"
name: "TerraformVM1"
network_id: <computed>
project: <computed>
root_disk_size: <computed>
security_group_ids.#: "1"
security_group_ids.3260590242: "84be7eef7-4pne-51c6-9abf6f3f9-c4zoek90887"
service_offering: "t1.pico"
tags.%: <computed>
template: "Debian 9 - Minimal - 64bits"
zone: "US-FL-MIAMI02-Z2-BASIC"
Plan: 1 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
Do you want to perform these actions?
Terraform will perform the actions described above.
Only 'yes' will be accepted to approve.
Enter a value: yes
cloudstack_instance.TerraformVM1: Creating...
display_name: "" => "<computed>"
expunge: "" => "true"
group: "" => "<computed>"
ip_address: "" => "<computed>"
keypair: "" => "MY_SSH_KEYPAIR"
name: "" => "TerraformVM1"
network_id: "" => "<computed>"
project: "" => "<computed>"
root_disk_size: "" => "<computed>"
security_group_ids.#: "" => "1"
security_group_ids.3260590242: "" => "84be7eef7-4pne-51c6-9abf6f3f9-c4zoek90887"
service_offering: "" => "t1.pico"
tags.%: "" => "<computed>"
template: "" => "Debian 9 - Minimal - 64bits"
zone: "" => "US-FL-MIAMI02-Z2-BASIC"
cloudstack_instance.TerraformVM1: Still creating... (10s elapsed)
cloudstack_instance.TerraformVM1: Still creating... (20s elapsed)
cloudstack_instance.TerraformVM1: Still creating... (30s elapsed)
cloudstack_instance.TerraformVM1: Still creating... (40s elapsed)
cloudstack_instance.TerraformVM1: Creation complete after 46s (ID: ba1220fc-b777-48e2-b63a-5d21ccc930ba)
Apply complete! Resources: 1 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
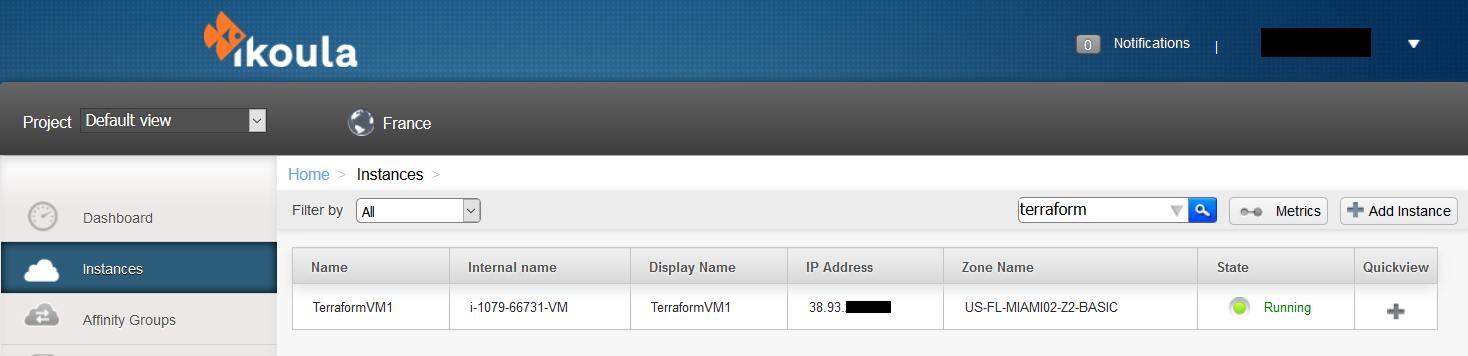
Ici nous venons de déployer en quelques secondes, une instance nommée "TerraformVM1" avec le modèle "Debian 9 - Minimal - 64bits" dans la zone basic "US-FL-MIAMI02-Z2-BASIC" avec l'offre de calcul "t1.pico".
Nous pouvons voir celle-ci depuis notre interface Cloud Ikoula One :
Nous pouvons nous connecter sur notre instance fraichement déployée. Note : Pour que cela fonctionne il faut que le groupe de sécurité dans lequel nous avons déployé le permette, sinon il faudra y rajouter une règle autorisant la connexion.
$ ssh -i MY_SSH_KEYPAIR root@38.93.X.X The authenticity of host '38.93.X.X (38.93.X.X)' can't be established. ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:4D7s+xxxXXXXxxxxXXXXXXXXXxxxxXXXXXxxXXXXxxXXXxxx. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes Warning: Permanently added '38.93.X.X' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts. Linux TerraformVM1 4.9.0-8-amd64 #1 SMP Debian 4.9.110-3+deb9u4 (2018-08-21) x86_64 The programs included with the Debian GNU/Linux system are free software; the exact distribution terms for each program are described in the individual files in /usr/share/doc/*/copyright. Debian GNU/Linux comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by applicable law. root@TerraformVM1:~#
Pour supprimer notre instance, il nous suffira d'exécuter la commande "terraform destroy" et valider en saisissant "yes" quand cela nous est demandé :
$ terraform destroy cloudstack_instance.TerraformVM1: Refreshing state... (ID: ba1220fc-b777-48e2-b63a-5d21ccc930ba) An execution plan has been generated and is shown below. Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols: - destroy Terraform will perform the following actions: - cloudstack_instance.TerraformVM1 Plan: 0 to add, 0 to change, 1 to destroy. Do you really want to destroy? Terraform will destroy all your managed infrastructure, as shown above. There is no undo. Only 'yes' will be accepted to confirm. Enter a value: yes cloudstack_instance.TerraformVM1: Destroying... (ID: ba1220fc-b777-48e2-b63a-5d21ccc930ba) cloudstack_instance.TerraformVM1: Still destroying... (ID: ba1220fc-b777-48e2-b63a-5d21ccc930ba, 10s elapsed) cloudstack_instance.TerraformVM1: Destruction complete after 15s Destroy complete! Resources: 1 destroyed.